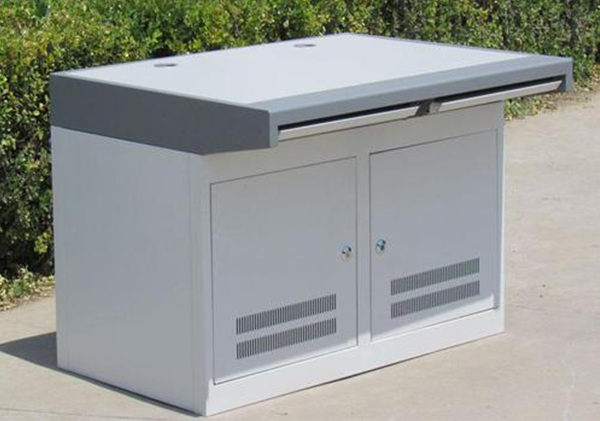
Using a high-energy density laser beam to heat the workpiece rapidly increases the temperature, reaching the boiling point of the material in a very short period of time, and the material begins to vaporize, forming vapor. The ejection speed of these vapors is very high, and at the same time as the vapors are ejected, incisions are formed on the material. With the continuous development of the storage tank industry, more and more industries and enterprises are using laser cutting (3 sheets) for storage tanks. More and more enterprises are entering the storage tank industry. However, due to the reduction of the cost of subsequent process processing, it is still feasible to use this equipment in large-scale production.
brief introduction
Laser cutting equipment can cut stainless steel below 4mm, and adding oxygen to the laser beam can cut carbon steel with a thickness of 20mm. However, after oxygen cutting, a thin oxide film will form on the cutting surface. The cutting thickness can be increased to 20mm, but the size error of the cutting parts is relatively large.
The price of laser cutting equipment is quite expensive, about 1.5 million yuan or more. However, due to the reduced cost of subsequent processing, it is still feasible to use this equipment in large-scale production. Due to the lack of cutting tool processing costs, laser cutting equipment is also suitable for producing small batches of various sizes of parts that could not be processed before. Laser cutting equipment usually uses computerized numerical control technology (CNC) devices, which can be used to receive cutting data from computer-aided design (CAD) workstations via telephone lines.

principle
Laser cutting is the use of a focused high-power density laser beam to irradiate a workpiece, causing the irradiated material to quickly melt, vaporize, burn, or reach the ignition point. At the same time, high-speed airflow coaxial with the beam is used to blow away the molten material, thereby achieving the cutting of the workpiece. Laser cutting is one of the thermal cutting methods.

 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque