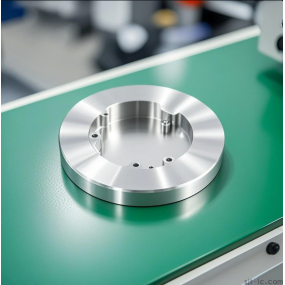
Feeling overwhelmed by all the talk about CNC machines? 🤯 You know they can make parts with crazy precision, but when it comes to figuring out which one you actually need for your project or business, you're stuck asking, "What are the different types of CNC Machining machinery, anyway?" Don't worry, you're not alone. This guide is here to cut through the confusion and break down the main types in plain English.

So, What ARE the Main Types of CNC Machines?
At its heart, a CNC machine is just a robot that follows digital instructions to cut material. The big difference comes from how they move and what they cut. For most people, the main ones you'll encounter are CNC Mills, CNC Lathes, and CNC Routers. Think of it like this: a mill generally moves the cutting tool around a stationary block of material, a lathe spins the material against a stationary tool, and a router is like a heavy-duty, super-precise version of a woodworker's router. But let's get into the details.
1. CNC Milling Machines: The All-Rounders 🛠️
If you need to make pockets, holes, slots, or complex 3D shapes out of a solid block, a CNC mill is your best friend. The part sits on a table, and a spinning cutter comes down from above to carve it. It's incredibly versatile.
What they're great for:
- Creating engine blocks or complex brackets.
- Making molds for plastic injection.
- Prototyping just about any mechanical part.
I've found that while mills can do a ton, they might not be the fastest choice for making a bunch of identical, simple round parts. That's where another machine comes in...
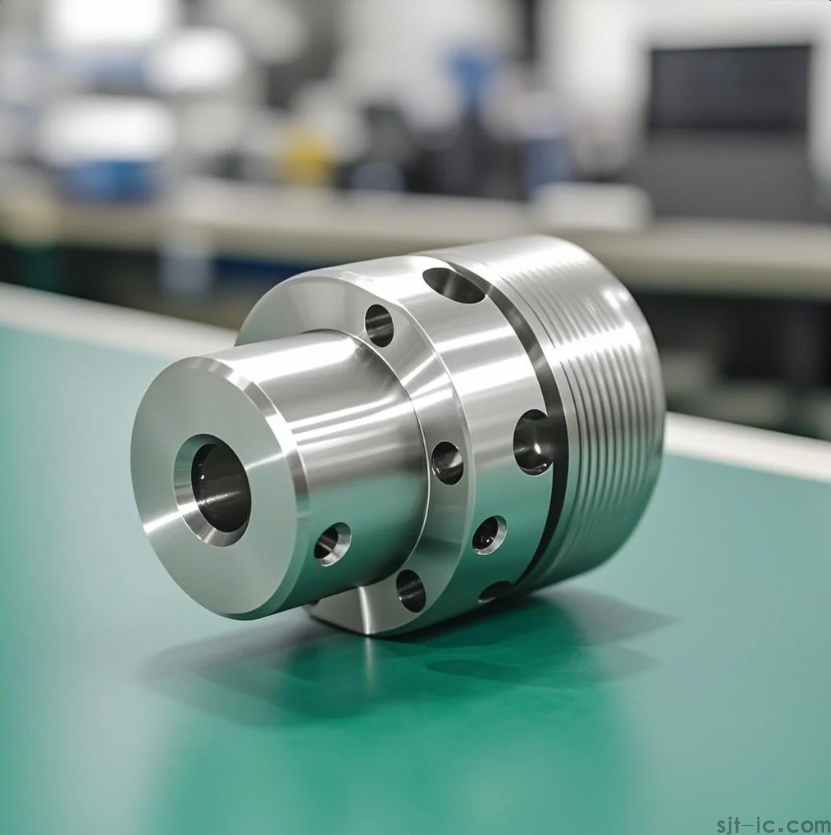

2. CNC Lathes: Masters of Round Parts 🔄
Also called "CNC Turning Centers," these machines are specialists. They hold a piece of material and spin it at high speed. Then, a stationary cutting tool presses against it to shave away material, creating cylindrical or conical shapes.
What they're perfect for:
- Shafts, bolts, and bushings.
- Baseball bats and table legs.
- Any part that has symmetry around a central axis.
Honestly, the precision you can get on a modern lathe is mind-blowing. However, if your part is flat, sheet-like, and needs cutting out, you'd be looking at a different beast entirely.

3. CNC Routers: For the Big and (Mostly) Soft Stuff 📏
You can think of a CNC router as a cousin to the mill. It often has a larger work area and is built to handle softer materials, though many can tackle aluminum these days. They are staples in woodworking and sign-making shops.
Common uses include:
- Cutting out wooden furniture parts.
- Engraving signs and logos.
- Creating intricate patterns on acrylic or foam.
They are fantastic for their intended purpose, but I wouldn't try to machine a tough titanium aerospace part on one. The rigidity just isn't the same as an industrial mill.
Wait, There's More: Other Machines You Should Know
The three above are the core, but the world of automated machinery is vast. It's worth mentioning a couple of other key players that solve specific problems.
CNC Plasma Cutters: These use a super-hot jet of plasma to slice through electrically conductive metals like steel and aluminum. They are blazingly fast for cutting 2D profiles from sheet metal.
CNC EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): This one is wild. It uses electrical sparks to erode material, which allows it to cut incredibly hard metals and create shapes that would be impossible with a traditional cutter. It's a slower process, but for some jobs, it's the only way.
So, the "best" machine isn't a single answer. It's a question of what you're making, what you're making it from, and how many you need. This variety of equipment is what makes modern manufacturing so powerful.
How to Choose the Right One for Your Needs? 🤔
This is the million-dollar question. Picking the wrong machine can waste time and money. You need to think about a few key things.
Material Type: Are you cutting metal, wood, or plastic? This is your first and most important filter.
Part Complexity: Simple 2D shapes? A router or plasma cutter might work. Intricate 3D parts? You're likely in mill territory.
Part Geometry: Is it round? A lathe is probably your answer. Is it a block? Look at a mill.
Budget and Volume: This is the real-world decider. A hobbyist router costs a few thousand, while a 5-axis industrial mill can cost more than a house.
Navigating these choices can be tricky. Sometimes, the best move is to just talk to an expert who has seen it all.
Still unsure which type of CNC machining machinery is the perfect fit for your specific component? Get a professional opinion. Our technical specialists can help you figure out the most efficient and cost-effective way to bring your design to life. Reach out to our team online for a free consultation today!
// A little-known fact: The flexibility of modern 5-axis CNC mills might be reducing the number of separate setups needed for a complex part, perhaps blurring the lines between traditional machining categories.

 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque