I. Opening Scenario: Are You Also Wondering How Quotations Are Calculated?
"I asked three factories for quotes on the same batch of parts, and the prices differ by 30%! Which one is reliable anyway?" — The editor often receives such complaints 😅. In fact, the difference in quotes stems from different calculation logics. Some hide management fees, while others omit tool wear costs... So today, we will break down the formula to help you fully understand quotations!
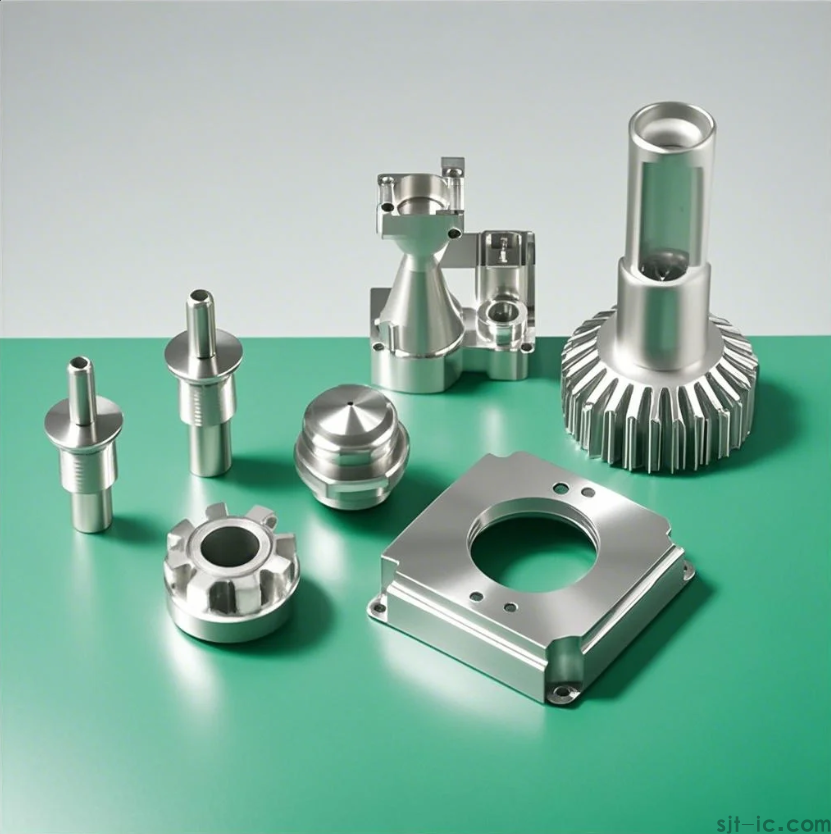

II. Core Formula: CNC Machining Unit Price = Material Cost + Processing Cost + Surface Treatment Cost + Management Fee + Profit
This formula is the industry standard, but the details of each item are the key! Let the editor give an example:
- Material Cost: If aluminum is priced at 20 yuan/kg, a 0.5kg part will cost 10 yuan. Formula: Material Unit Price × Weight
- Processing Cost: This is the major component! It involves equipment working hours and tool wear. Formula: Processing Time × Machine Hour Rate + Tool Cost
A note from the editor: Many beginners only ask about material prices but ignore processing time. In fact, for complex parts, working hours may account for 60% of the total cost!
III. Detailed Explanation of Processing Cost: How to Calculate Time? How to Determine the Rate?
1. Basis for Calculating Working Hours
- Part Complexity: A simple slot or hole may take 0.5 hours per part, while multi-curved shapes can take up to 2 hours per part.
- Precision Requirements: Finishing is required for tolerances within ±0.05mm, which doubles the time 😵.
- Equipment Differences: An ordinary milling machine costs 30 yuan/hour, while a 5-axis CNC machine can cost up to 100 yuan/hour.
2. Machine Hour Rate Table (Common Types)
| Equipment Type | Hourly Rate (Yuan) | Application Scenario |
|----------------------|--------------------|--------------------------------|
| Ordinary Lathe | 15-20 | Simple shaft parts |
| 3-Axis CNC Machine | 60-80 | Milling of medium-complexity parts |
| 5-Axis CNC Machine | 100-150 | High-precision curved surfaces |
| Wire Cutting Machine | 20-30 | Precision holes and slots |
→ Tip: The rate includes equipment depreciation, labor, and electricity costs, but don’t forget tool consumables! For example, the cost of one alloy cutter head may be allocated to 5 yuan per part.
IV. Surface Treatment and Hidden Costs: Don’t Be Deceived by Low Prices!
Comparison of Surface Treatment Costs
- Anodizing: Approximately 10-15 yuan per part (commonly used for aluminum parts)
- Sandblasting and Polishing: 15-20 yuan per part (used when glossiness is required)
- Electroplating: 30-50 yuan per part (wear-resistant but expensive)
Management Fee and Profit
- Management Fee: Usually 5%-15% of the processing cost.
- Profit: Generally fluctuates between 10%-30% of the total cost. Manufacturers may increase the price for small-batch orders because the setup time is allocated to fewer parts.
Editor’s Insight: A customer once chose the cheapest quote by comparing prices, but the surface anodizing cost was omitted. In the end, the unit price was 20% higher than expected... So be sure to confirm that the quote includes all items!
V. Q&A: Common Questions for Beginners
Q: Why is the unit price higher for my small-batch order?
A: Because the programming and setup time are allocated to a small number of parts! For example, 1 hour of setup + 0.5 hours of programming: for 10 parts, each part bears 0.15 hours; for 100 parts, each part only bears 0.015 hours. It’s an iron rule that the larger the batch, the lower the unit price!
Q: How much impact does different materials have?
A: A huge impact! Aluminum alloy generally costs 20-30 yuan/kg, while stainless steel costs 50-70 yuan/kg. Moreover, the processing time increases by 30% (because its high hardness causes more tool wear).
VI. Money-Saving Tips: Summarized from the Editor’s Years of Observation
1. Simplify the Design: Reduce curved surfaces and precision structures to directly lower working hours.
2. Place Bulk Orders: It’s not a dream to save 50% by combining orders for production instead of placing scattered orders ✨.
3. Choose Basic Surface Treatment: replace electroplating with ordinary anodizing to reduce costs by 60%.
4. Provide Clear Drawings: Reduce communication errors and costs caused by repeated modifications.
Final Reminder: Be sure to obtain a detailed quotation sheet! A reliable supplier will list each cost item clearly. Hope this article helps you, and you won’t be confused when inquiring about prices next time!
Do you need me to further optimize the translation of certain sections, such as adjusting the wording of professional terms to be more in line with international CNC machining industry habits, or generate a bilingual comparison table of core CNC machining cost terms?

 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque