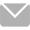
The process flow in the operation of a CNC five axis machining center is a complex and delicate process, involving multiple key steps from workpiece preparation to machining completion. The following is a detailed analysis of the process flow: 1. Preliminary preparation: ① Selection of workpieces and materials: Determine the workpieces to be processed and the required materials, considering the physical properties, processing difficulty, and cost of the materials.  ② Workpiece clamping and positioning: Fix the workpiece to be processed on the workbench and perform precise positioning through fixtures. This step is crucial for ensuring machining accuracy Tool and fixture selection: Choose appropriate tools and fixtures based on the shape, size, and processing requirements of the workpiece. The selection of cutting tools should take into account cutting efficiency, tool life, and machining quality. 2、 Programming and Simulation ① Machining Program Development: Use CAD/CAM software to develop machining programs based on the design drawings of the workpiece. The machining program contains information such as the motion trajectory and cutting parameters of each axis required for workpiece machining Tool path simulation: Simulate the generated tool path, check whether it is reasonable and perfect, and ensure that there will be no collision or interference problems in actual machining NC program generation and simulation: Convert the simulated tool path file into an NC program and perform NC program simulation or physical simulation to further verify the correctness of the program and the machining effect. 3、 Processing process ① Machine tool start-up and preheating: Turn on the machine tool power, start the CNC five axis machining center control system, preheat the heater, raise the temperature of the heater and heat exchanger, preheat the machine tool, and check whether each component is operating normally. ② Tool and fixture settings: The operator sets the tool and fixture according to the program, and performs automatic tool changing and automatic clamping work on the machine Processing execution: The control system reads the NC program and controls the movement of each axis according to the instructions in the program. By moving the X, Y, and Z axes and rotating the A, B, or C axes, precise positioning and cutting of the workpiece in three-dimensional space can be achieved Monitoring of machining process: During the machining process, the control system monitors the tool position, cutting force and other parameters in real time through sensors, and adjusts the machining parameters according to the actual situation to ensure the accuracy and quality of the machining Tool changing operation: When it is necessary to change the tool, the CNC five axis machining center can automatically perform the tool changing operation. This usually includes a series of actions such as extending the robotic arm, grabbing the tool, loosening the spindle, exchanging the tool, tightening the spindle, and resetting the robotic arm. 4、 Post processing ① Workpiece inspection: After processing is completed, the workpiece is inspected to ensure that its size, shape, and surface quality meet the design requirements. ② Machine tool maintenance and upkeep: Regularly clean and maintain various components of the CNC five axis machining center, such as tool libraries, fixtures, lubrication systems, etc. At the same time, regularly replace the lubricating oil and coolant of the machine tool to ensure its normal operation Data recording and analysis: Record various data during the machining process, such as machining time, cutting parameters, tool life, etc., and analyze them to optimize the subsequent machining process.
② Workpiece clamping and positioning: Fix the workpiece to be processed on the workbench and perform precise positioning through fixtures. This step is crucial for ensuring machining accuracy Tool and fixture selection: Choose appropriate tools and fixtures based on the shape, size, and processing requirements of the workpiece. The selection of cutting tools should take into account cutting efficiency, tool life, and machining quality. 2、 Programming and Simulation ① Machining Program Development: Use CAD/CAM software to develop machining programs based on the design drawings of the workpiece. The machining program contains information such as the motion trajectory and cutting parameters of each axis required for workpiece machining Tool path simulation: Simulate the generated tool path, check whether it is reasonable and perfect, and ensure that there will be no collision or interference problems in actual machining NC program generation and simulation: Convert the simulated tool path file into an NC program and perform NC program simulation or physical simulation to further verify the correctness of the program and the machining effect. 3、 Processing process ① Machine tool start-up and preheating: Turn on the machine tool power, start the CNC five axis machining center control system, preheat the heater, raise the temperature of the heater and heat exchanger, preheat the machine tool, and check whether each component is operating normally. ② Tool and fixture settings: The operator sets the tool and fixture according to the program, and performs automatic tool changing and automatic clamping work on the machine Processing execution: The control system reads the NC program and controls the movement of each axis according to the instructions in the program. By moving the X, Y, and Z axes and rotating the A, B, or C axes, precise positioning and cutting of the workpiece in three-dimensional space can be achieved Monitoring of machining process: During the machining process, the control system monitors the tool position, cutting force and other parameters in real time through sensors, and adjusts the machining parameters according to the actual situation to ensure the accuracy and quality of the machining Tool changing operation: When it is necessary to change the tool, the CNC five axis machining center can automatically perform the tool changing operation. This usually includes a series of actions such as extending the robotic arm, grabbing the tool, loosening the spindle, exchanging the tool, tightening the spindle, and resetting the robotic arm. 4、 Post processing ① Workpiece inspection: After processing is completed, the workpiece is inspected to ensure that its size, shape, and surface quality meet the design requirements. ② Machine tool maintenance and upkeep: Regularly clean and maintain various components of the CNC five axis machining center, such as tool libraries, fixtures, lubrication systems, etc. At the same time, regularly replace the lubricating oil and coolant of the machine tool to ensure its normal operation Data recording and analysis: Record various data during the machining process, such as machining time, cutting parameters, tool life, etc., and analyze them to optimize the subsequent machining process.
Hello! Welcome to EMAR's website!
 English
English » »
» »
 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque