CNC numerical control lathe machining is a highly automated precision machining method, and its whole process technology from programming to finished product can be summarized as the following key steps:
First, the programming stage
1. CAD design and CAM programming: First, use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to draw a three-dimensional model of the part and generate engineering drawings accordingly. Then, use Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to write a numerical control machining program according to the drawings and machining requirements, which describes the tool path, cutting parameters and machining sequence in detail.
2. Program simulation verification: In the environment of programming software or combined with numerical control simulation software, the program is fully simulated and verified to ensure that the definition of tools, machine tools and workpieces is accurate, the processing method is reasonable and there is no collision interference.
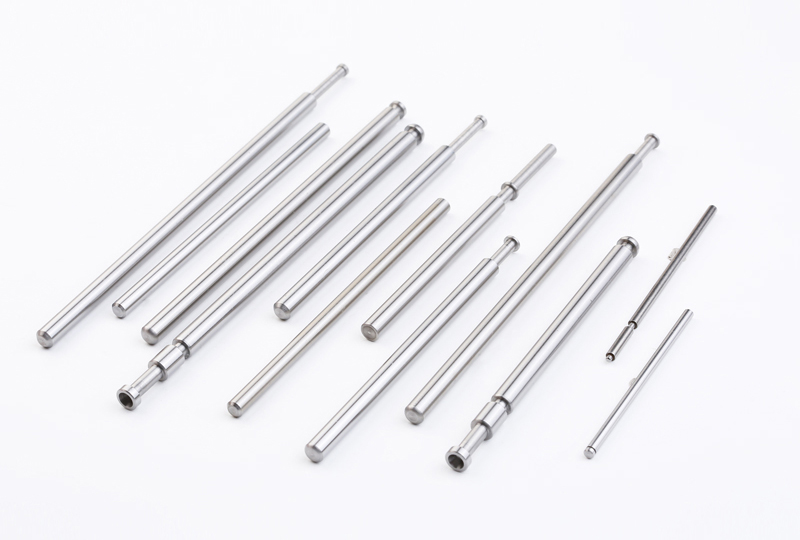 Preparation before processing
Preparation before processing
1. Equipment debugging: Check whether the various components of the machine tool are operating normally, including the spindle, guide rail, lubrication system, etc., and perform necessary maintenance and calibration.
2. Tool and fixture selection: Select the appropriate tool and fixture according to the processing requirements, and ensure that the tool is sharp and firmly fixed on the machine tool, so that the fixture can firmly fix the workpiece.
III. Formal processing
1. Workpiece clamping: Place the workpiece to be processed on the machine tool table and fix it with a fixture.
2. Tool setting and test cutting: adjust the tool position and angle, perform tool setting operations, and perform test cutting to verify the correctness of the program.
3. Start processing: After confirming that the preparatory work is ready, start the machine tool to start formal processing. During the processing process, the running status of the machine tool needs to be monitored throughout the process to ensure the safety and stability of the processing process.
 IV. Post-processing
IV. Post-processing
1. Quality inspection: Use precision measuring tools to inspect the quality of the finished parts, including size, shape, and surface roughness.
2. Disassembly and cleaning: Disassemble the fixture and workpiece, and clean and maintain the machine.
Through the above steps, CNC numerical control lathe machining can efficiently and accurately complete the whole process from programming to finished product.

 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque