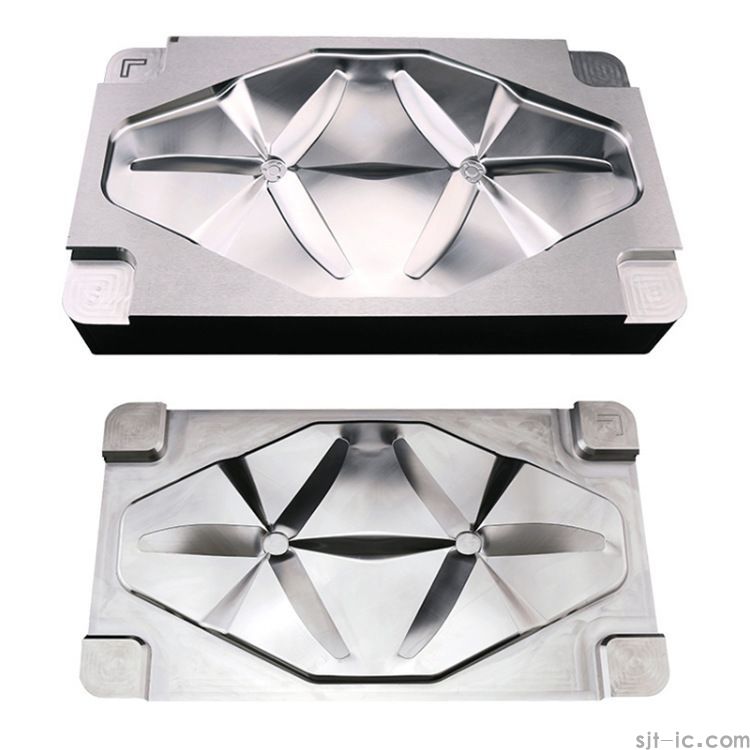
Precision casting molds are the cornerstone of high-end manufacturing 🔩, yet traditional processes generally face three major pain points: insufficient precision, long delivery cycles, and high costs. Through digital control, CNC Machining technology perfectly meets the strict requirements of precision casting molds for complex structures, tight tolerances (±0.01mm), and surface finish.

🔍 I. Why Must Precision Casting Rely on CNC Technology?
1. Precision Assurance: CNC machines can achieve micron-level machining, avoiding dimensional deviations caused by traditional manual mold repair.
2. Complex Structure Handling: Multi-axis linkage (e.g., 5-axis CNC) enables machining of special-shaped structures such as deep cavities and inclined holes, reducing parting line issues.
3. Material Adaptability: Suitable for common casting materials like stainless steel, titanium alloys, and aluminum alloys; cutting efficiency can be optimized by adjusting parameters through programming.
💡 Industry Insight: In the fields of high-end medical devices and aerospace, 90% of precision casting molds have adopted CNC machining to replace traditional processes.
⚙️ II. Full-Process Analysis of CNC Machining for Precision Molds
1. 3D Modeling and Programming
- Use software such as UG and Pro/E to generate 3D models and write G-code to control tool paths.
- Key Point: Tool path planning must avoid over-cutting, and reserve finishing allowances (usually 0.2-0.5mm).
2. Rough Machining and Finishing
- Rough machining uses large-diameter tools for rapid material removal; finishing uses high-speed milling cutters to achieve a surface finish of Ra ≤ 0.8μm.
- Technical Detail: During finishing, cutting temperature must be controlled to prevent thermal deformation of the material.
3. Quality Inspection and Post-Processing
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) conducts full-dimensional inspection, focusing on verifying cavity tolerances and draft angles.
- Surface Treatment: Processes like Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) are used to refine textures or remove burrs.
🌐 III. Industry Application Scenarios and Demand Breakthroughs
| Industry | Core Requirements | CNC Solutions |
|-------------------|-----------------------------------|----------------------------------------|
| Medical Devices | Sterile surfaces, zero defects | Mirror polishing + 5-axis micro-hole machining |
| Auto Parts | High temperature resistance, high strength | High-speed cutting with carbide tools |
| Aerospace | Lightweight and structural integration | Multi-axis linkage machining of titanium alloys |
💎 Case Sharing: After a new energy vehicle gear mold adopted 5-axis CNC machining, its service life increased from 50,000 cycles to 150,000 cycles, and costs decreased by 30%.
💡 IV. How to Optimize CNC Machining Efficiency and Costs?
- Tool Management: Use carbide-coated tools to extend service life by more than 20%.
- Programming Strategy: Simulate the cutting process through CAM software to reduce idle tool paths and improve efficiency by 15%-30%.
- Equipment Selection: For small-to-medium batch production, vertical machining centers (VMC) are recommended; for large-batch production, horizontal machining centers (HMC) are preferred.
🚀 V. Future Trend: Integration of Intelligence and Additive Manufacturing
CNC technology is evolving toward smart factories:
- Real-time monitoring systems predict tool wear through sensors and automatically adjust parameters.
- The composite process of metal 3D printing + CNC finishing enables integrated manufacturing of complex cooling channels.
🌟 Exclusive View: In the next 5 years, AI-based adaptive machining will replace 50% of traditional CNC programming modes, realizing "zero-adjustment production".

 Spanish
Spanish Arabic
Arabic French
French Portuguese
Portuguese Belarusian
Belarusian Japanese
Japanese Russian
Russian Malay
Malay Icelandic
Icelandic Bulgarian
Bulgarian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Estonian
Estonian Irish
Irish Polish
Polish Persian
Persian Boolean
Boolean Danish
Danish German
German Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch Galician
Galician Catalan
Catalan Czech
Czech Croatian
Croatian Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Romanian
Romanian Maltese
Maltese Macedonian
Macedonian Norwegian
Norwegian Swedish
Swedish Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Welsh
Welsh Urdu
Urdu Ukrainian
Ukrainian Greek
Greek Hungarian
Hungarian Italian
Italian Yiddish
Yiddish Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Spanish Basque
Spanish Basque